Sales : Brief Overview with Examples
Definition of Sales with Examples

Sales is the process of connecting people with products or services that meet their needs or solve their problems. It’s about understanding what customers are looking for, guiding them through the decision-making process, and ensuring they feel confident in their purchase. Successful sales don’t just focus on selling a product; they focus on building trust and relationships. Whether it’s through a simple exchange or a long-term partnership, the essence of sales lies in delivering value to both the buyer and the seller, resulting in mutual satisfaction.
According to Philip Kotler:
“Sales is the process by which organizations align their products and services to the requirements and wants of customers, to earn revenue and achieve business growth.”
According to C.K. Prahalad:
“Sales is about creating value for customers and helping them achieve their goals. It’s not about pushing products, but about delivering solutions that make a difference.
Example of Sales
The sales team identifies potential customers by analyzing website traffic, running social media ads, and offering free sample requests. One day, a new lead signs up for a sample box of their healthy snack range.
The sales representative reaches out to the customer through email to gather feedback and learn more about their preferences. The rep then schedules a call to explain the benefits of their organic snacks, focusing on the customer’s interest in healthy, sustainable food.
After the call, the sales rep enters notes in their CRM and sets reminders to follow up. A few days later, they send an email offering a discount on the customer’s first subscription box purchase. The customer is interested but wants more information on different snack options and pricing.
The sales rep shares more details, addressing any concerns about product variety and pricing. Eventually, the customer decides to subscribe to the monthly snack box.
Once the sale is complete, the rep introduces the customer to their support team for any future inquiries and sends a thank-you email. The customer is now part of the company’s loyalty program for future engagement.
Types of Sales
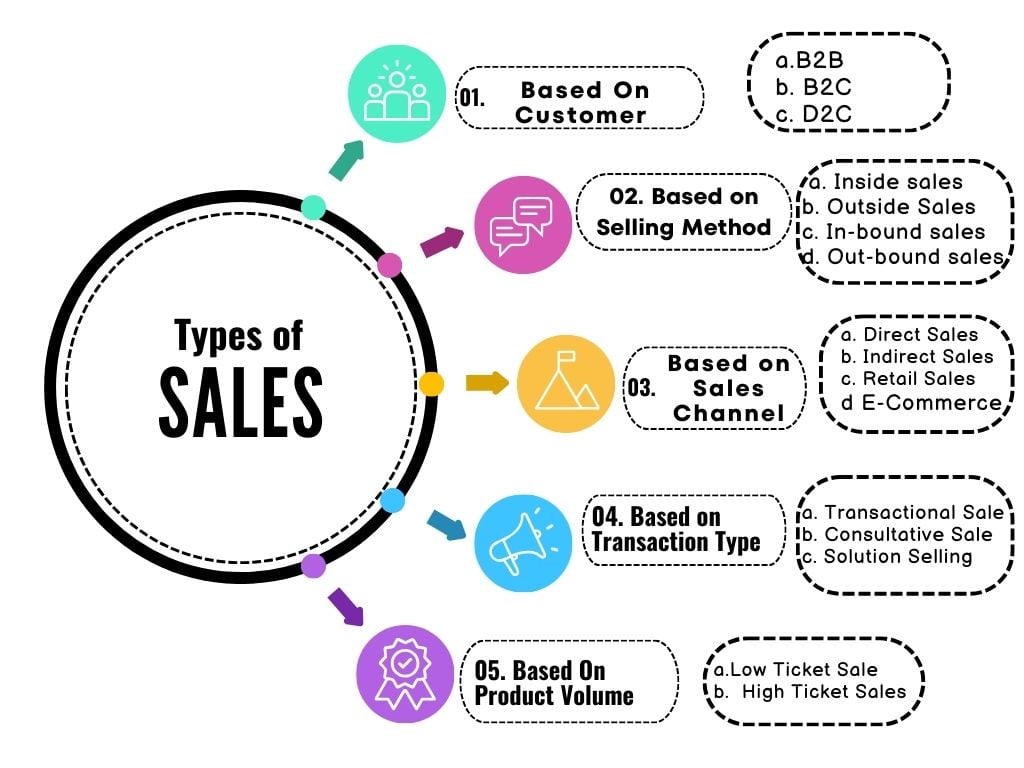
1. Based on Customer Type:
b. B2C (Business to Consumer) Sales : B2C sales happen when businesses sell directly to individual consumers. This type of sale focuses on fast decision-making, convenience, and a higher volume of sales. Examples include online shopping, retail purchases, and personal services.
c. D2C (Direct to Consumer) Sales : In D2C sales, companies cut out the middlemen (like retailers) and sell directly to customers. It’s mostly done through online stores or brand-owned physical outlets. This allows businesses to have more control over pricing, customer experience, and product delivery
2. Based on Selling Method:
b. Outside Sales (Field Sales) : In outside sales, sales reps meet clients in person. It’s typically used for larger, more complex sales like pharmaceutical products or large B2B deals, where relationship-building and face-to-face meetings are crucial.
c. Inbound Sales : Inbound sales involve responding to potential customers who have already shown interest through marketing channels. The focus is on guiding these leads towards a purchase by addressing their needs.
d. Outbound Sales : Outbound sales involve proactively reaching out to potential customers, using tactics like cold calling or emailing. The aim is to generate interest and convert these contacts into buyers.
3. Based on Sales Channel:
b. Indirect Sales : Indirect sales involve selling products through intermediaries like retailers, distributors, or agents. This is commonly used in industries like FMCG and manufacturing, where wide distribution networks are essential to reach more customers.
c. E-Commerce Sales : E-commerce sales are conducted through websites, apps, or other online platforms. It’s a growing trend due to the convenience and ease of shopping online, offering a wider audience reach and 24/7 accessibility.
d. Retail Sales : Retail sales occur in physical stores, where customers can personally interact with products before buying them. This type of sale is common in consumer goods industries and allows for immediate purchases and personal customer service.
4. Based on Transaction Type:
b. Consultative Sales : In consultative sales, the salesperson acts as a trusted advisor, understanding the customer’s needs in-depth and offering solutions tailored to their unique problems. This approach builds trust and adds value beyond just selling a product.
c. Solution Selling : Solution selling is a type of consultative selling where the focus is on solving a specific problem the customer is facing. The salesperson provides a product or service that directly addresses the customer’s pain points.
d. Relationship-Based Sales : This type of sale prioritizes building long-term relationships with customers. The goal is to earn customer loyalty and ensure repeat business, which is especially important for high-end or premium products and services.
5. Based on Product Pricing or Volume:
b. High-Ticket Sales : High-ticket sales refer to selling expensive, high-value products or services. These sales require more effort, personalized interactions, and often involve longer decision-making cycles. Building strong relationships and trust with customers is key. Examples include luxury goods, real estate, or premium services.
Importance of Sales
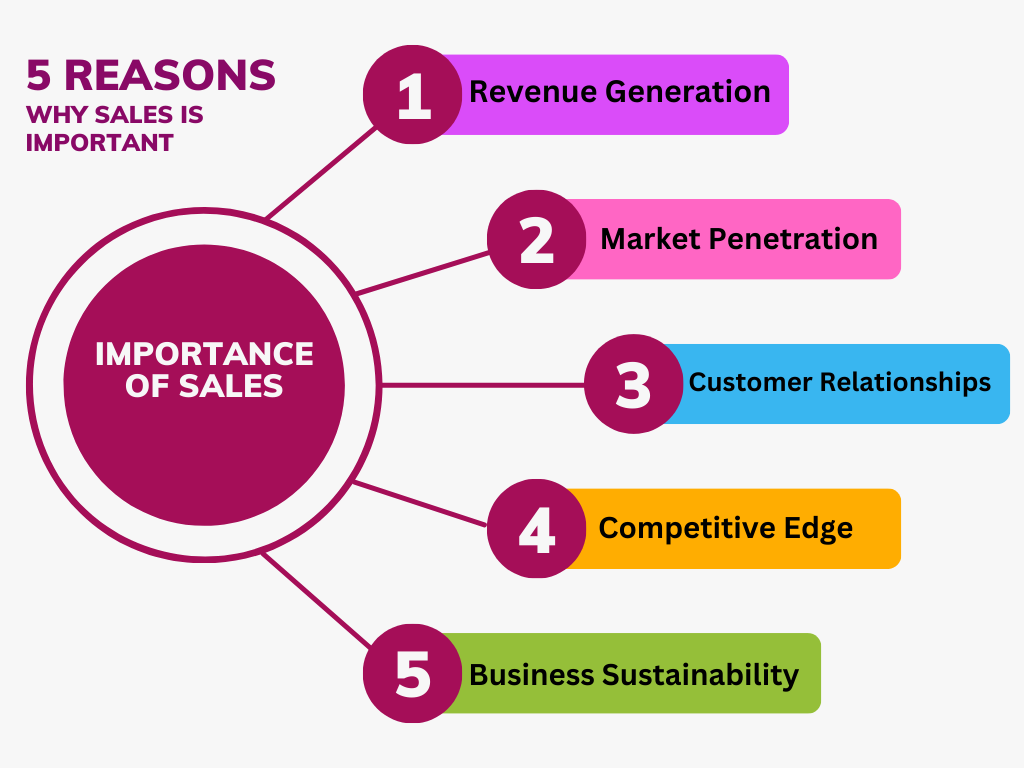
1. Revenue Generation:
Example – Imagine a local bakery. Every loaf of bread or pastry sold generates revenue, which keeps the bakery’s lights on, pays employees, and allows for growth, like opening new locations or adding new products.
2. Market Penetration:
Example – Consider a tech startup launching a new app. By using targeted sales strategies, such as partnerships or special promotions, the app reaches new users and markets, expanding its user base and creating new revenue streams.
3. Customer Relationships:
Example – Think of a high-end fashion retailer that provides personalized shopping experiences. By understanding customer preferences and offering tailored recommendations, the retailer builds strong relationships, encouraging repeat purchases and fostering brand loyalty.
4. Competitive Edge:
Example – Take Nike, for example. Through innovative sales tactics and branding, Nike stands out in the crowded sportswear market. Their exceptional sales strategies and strong brand identity help them maintain a leadership position over competitors.
5. Business Sustainability:
Example – Envision a subscription-based streaming service. By consistently attracting and retaining subscribers, the service ensures a steady flow of income, which supports ongoing operations, content creation, and long-term growth.
Common Terms Uses in Sales
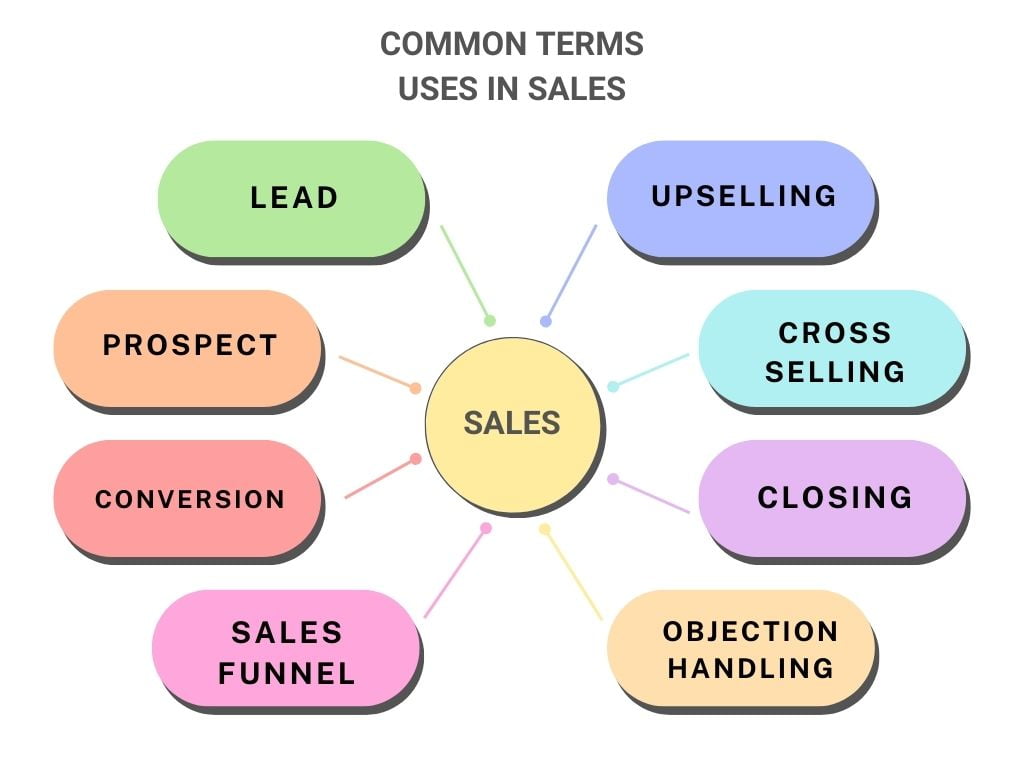
1. Lead:
- A potential customer who has shown interest in your product or service. Leads are the starting point of the sales process.
- Example: Someone who signs up for your newsletter is a lead.
2. Prospect:
- A lead that fits your ideal customer profile and is likely to buy. Prospects are usually qualified based on specific criteria.
- Example: A lead who actively engages with your sales content becomes a prospect.
3. Conversion:
- The action of turning a lead or prospect into a paying customer. It’s the goal of the entire sales funnel.
- Example: When a prospect purchases your product, it’s a conversion.
4. Sales Funnel:
- A step-by-step process that leads a prospect from initial awareness to the final purchase. It helps visualize where customers are in their buying journey.
- Example: Awareness → Interest → Decision → Purchase.
5. Upselling:
- A step-by-step process that leads a prospect from initial awareness to the final purchase. It helps visualize where customers are in their buying journey.
- Example: Awareness → Interest → Decision → Purchase.
6. Cross - Selling:
- Offering related or complementary products to a customer. It increases the value of the purchase.
- Example: Suggesting a beverage when a customer buys snacks.
7. Objection Handling:
- Addressing and resolving potential customers’ concerns or doubts to keep the sales conversation moving forward.
- Example: Clarifying product features to ease a customer’s worry about compatibility.
8. Close:
- The final stage of a sales process when the deal is sealed, and the prospect becomes a customer.
- Example: Signing a contract or receiving payment marks the close of a deal.
Sales Ethics
What is Sales Ethics
Examples of Sales Ethics
By focusing on what benefits the customer, the salesperson practices ethical sales, ensuring a fair transaction while enhancing the company’s reputation.
Importance of Sales Ethics
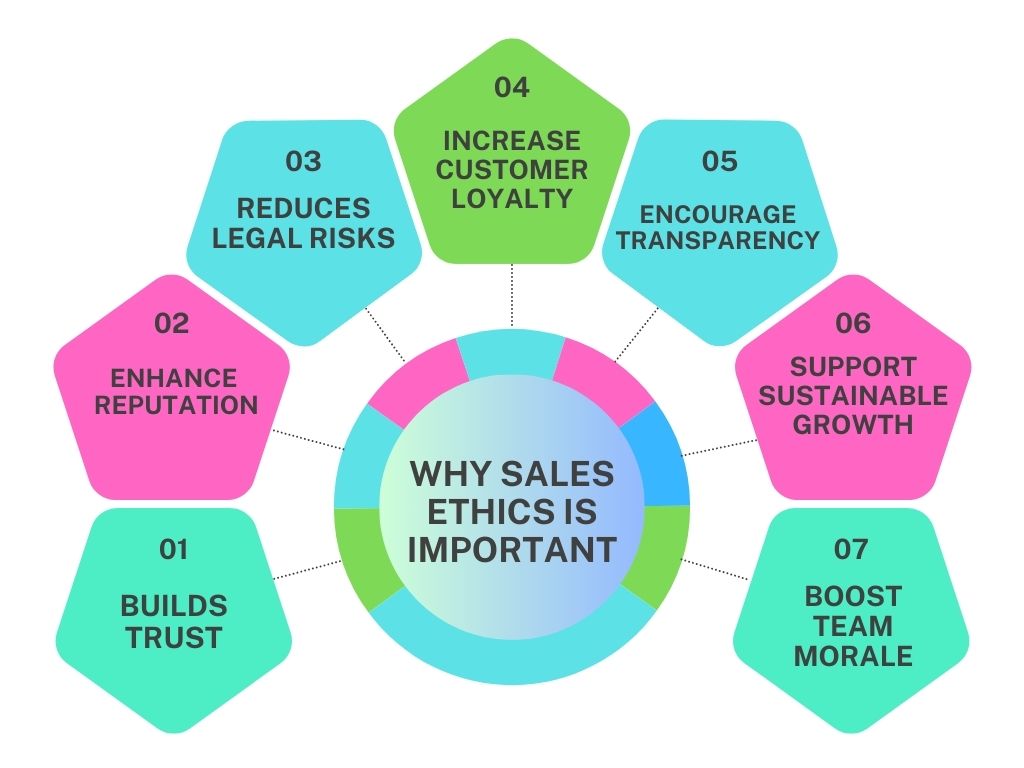
1. Builds Trust:
- Ethical sales practices create trust between you and the customer, making them feel secure in their decision.
- Example: A salesperson honestly explains both the benefits and limitations of a product, building credibility with the customer.
2. Enhances Reputation:
- Companies known for ethical sales gain a positive reputation, which helps attract new customers and retain current ones.
- Example: A business that never oversells or misleads customers is likely to be recommended by satisfied buyers.
3. Reduces Legal Risks:
- Ethical practices help avoid legal problems, as the company remains compliant with laws and regulations.
- Example: Selling products without false claims about their performance avoids potential lawsuits.
4. Increases Customer Loyalty:
- Ethical behavior fosters loyalty as customers trust companies that are honest and treat them well.
- Example: A customer continues to buy from a company that prioritizes their needs over just making a sale.
5. Encourages Transparency:
- Ethical sales promote transparency, helping customers make informed decisions, which increases satisfaction.
- Example: A company clearly states the full pricing upfront, with no hidden fees.
6. Supports Sustainable Growth:
- Ethical sales drive long-term business growth by focusing on real customer needs instead of quick profits.
- Example: Offering the right product for a customer’s needs ensures repeat business and referrals.
7. Boosts Team Morale:
- A strong ethical culture improves team morale, as employees feel proud of their work and the company.
- Example: Sales teams feel motivated when they know they are not pressured into unethical practices, leading to a healthier work environment.
Future Trends in Sales
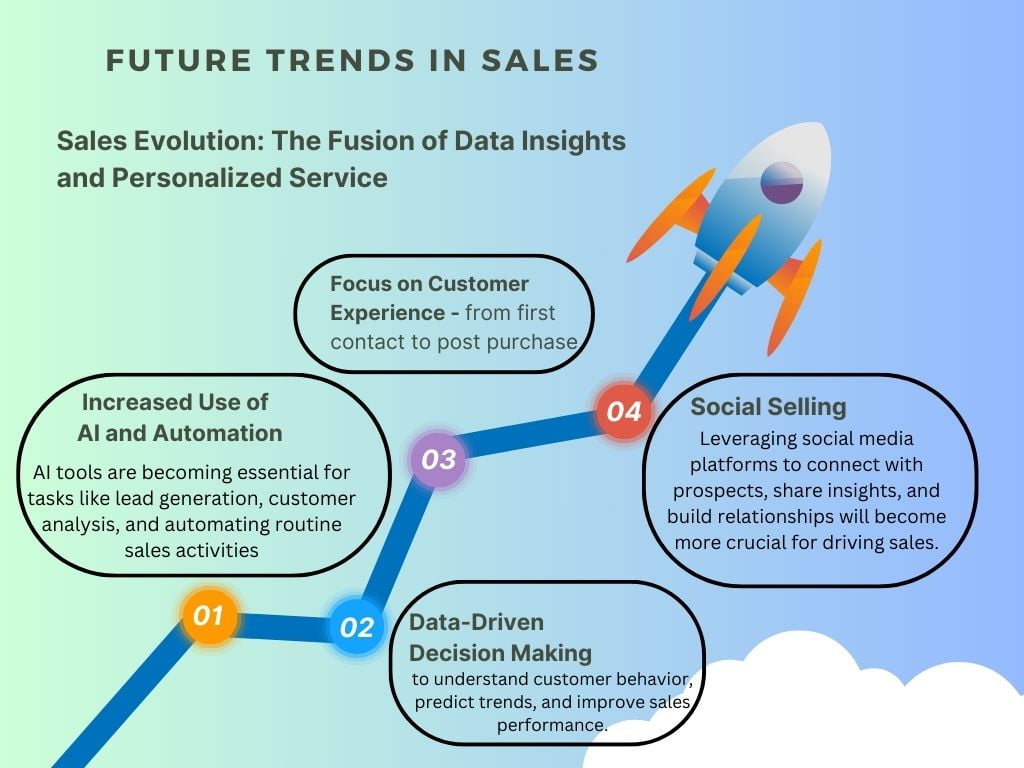
1. AI and Automation: Boosting Efficiency
2. Data Driven Sales: Precision Targeting
3. Customer Experience: Creating Loyalty
4. Social Media: Building Authentic Connections
Conclusion : What is sales in simple words with example
Sales is the backbone of any successful business. It’s not just about making transactions; it’s about understanding the customer’s needs, delivering value, and building trust. As technology and consumer behavior evolve, so do the strategies and tools salespeople use. From mastering key skills like communication and negotiation to embracing digital tools and ethical practices, success in sales requires constant learning and adaptability. By staying ahead of trends, nurturing relationships, and maintaining a customer-centric approach, businesses can not only meet their sales targets but also foster long-term growth and loyalty.






