Case Study on Starbucks Coffee
Case study on starbucks coffee: A Brewing Success Story- 53 Years of Coffee Excellence
Starbucks Coffee Case Study: Strategy, Success, and Future Growth

Key Data Points (As of 2023)
Revenue: $36B
Stores: Over 37,000 globally, 16,000 in the US
Employees: Over 400,000 globally
Digital Engagement: 31 million active US members in Starbucks Rewards
Market Cap: Over $150B
Global Coffee Market Share: 40% (US), dominant in premium coffee
History Of Starbucks

During this time, the organization sold simmered, entire espresso beans. During its first year of activity, Starbucks bought green espresso beans from Peet’s, and then started purchasing legitimately from producers.
Starbucks Expansion Journey
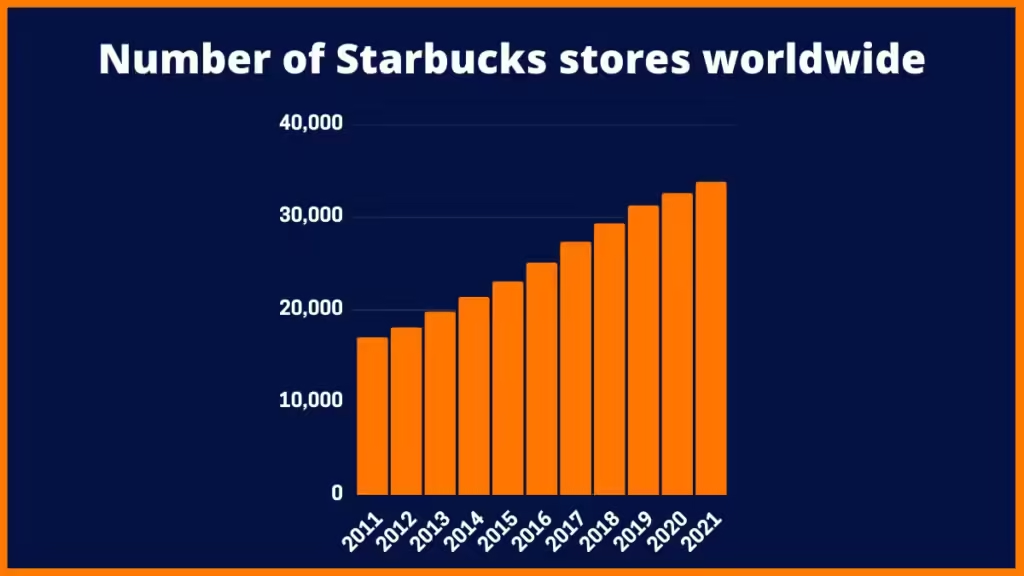
In 1987, Howard Schultz purchased Starbucks, rebranding his Il Giornale coffee shops as Starbucks and expanding rapidly. By 1989, Starbucks had 46 stores across the Northwest and Midwest, roasting over 2 million pounds of coffee annually. When Starbucks went public in 1992, it had 140 stores and $73.5 million in revenue. The company’s value reached $271 million, and its stock price surged by 70% within a few months of the IPO.
In July 2013, more than 10% of in-store purchases were made via mobile using the Starbucks app. Later that year, Starbucks launched the “Tweet-a-Coffee” campaign, allowing users to gift a $5 card via Twitter. By December 2013, 27,000 people participated, generating $180,000 in sales.
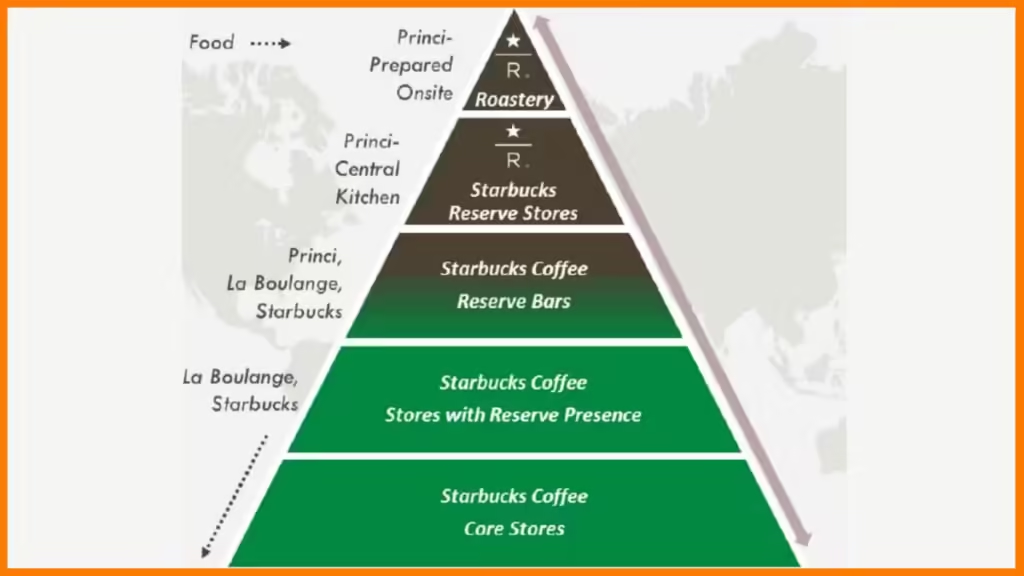
Business Model and Core Strategy
- Quantitative Example: The company’s commitment to ethical sourcing contributes to customer loyalty, as evidenced by its ability to charge premium prices — with an average beverage price of $4.75 compared to Dunkin’s $2.14.
Quantitative Analysis: Starbucks’ Financial Performance vs Competitors
Comparing Starbucks to its major competitors highlights its dominance:
Revenue: In 2023, Starbucks reported $36 billion in revenue, dwarfing Dunkin’ Brands (around $1.5 billion) and McDonald’s McCafé operations.
Net Profit Margin: Starbucks had a net profit margin of around 14%, higher than the industry average of 10%. Dunkin’s is lower due to its franchise model, while McDonald’s enjoys a higher margin because of real estate.
Global Market Share: Starbucks commands a significant 40% of the U.S. coffee shop market, followed by Dunkin’ Donuts with 26%.
Competitive Benchmarking: Starbucks consistently performs better than its closest competitors in terms of brand loyalty, premium pricing, and digital engagement.
Customer Segmentation: Understanding the Starbucks Consumer
Starbucks attracts a diverse range of customer segments, each contributing to its success:
- Affluent Millennials: This group prioritizes quality, ethical sourcing, and convenience. Starbucks’ premium offerings and focus on sustainability appeal strongly to them.
- Professionals: Many working professionals see Starbucks as an ideal “third place” where they can conduct meetings or work remotely.
- Health-Conscious Consumers: With growing demand for non-dairy, low-sugar options, Starbucks has adapted its menu to include plant-based alternatives like oat and almond milk.
- Tech-Savvy Users: A younger demographic of tech enthusiasts finds Starbucks’ mobile app and loyalty program highly engaging.
- Demographics: Starbucks’ core demographic in the U.S. includes 25-40-year-olds with an average income of $90,000+ per year.
- Behavioral Insights: 60% of Starbucks customers prefer personalized drinks, showing the importance of customization in their offerings.
Growth Opportunity: As Starbucks continues its expansion in markets like China and India, understanding the needs of these diverse and evolving customer segments is crucial for sustained growth.
Competitive Landscape:
Starbucks vs Major Players
- Dunkin’ Donuts: Known for affordability and quick service, Dunkin’ operates a franchise model. Its strength lies in a more accessible price point but lacks the premium branding Starbucks has.
- McCafé (McDonald’s): McCafé focuses on convenience with drive-thru coffee, leveraging McDonald’s real estate network. It offers cheaper alternatives but lacks Starbucks’ premium customer experience.
- Local Artisanal Coffee Shops: Local coffee shops offer niche experiences with a strong focus on community engagement and unique brewing techniques. This trend challenges Starbucks’ globalized model but also forces innovation at the premium end.
- Branding: Starbucks stands out as a luxury brand in the coffee market.
- Global Footprint: Its extensive global presence with over 37,000 stores makes it accessible, yet retains its premium appeal.
- Product Innovation: Seasonal beverages (e.g., Pumpkin Spice Latte) and premium coffee experiences, such as the Reserve Roastery, allow Starbucks to cater to both mass and niche markets.
Technological Innovation: A Key to Starbucks' Success
- Impact: As of 2023, 25% of all U.S. Starbucks transactions were made through the mobile app. The app not only enhances convenience but also gathers customer data for personalized marketing.
- Example: In 2023, Starbucks used AI-driven predictive analytics to tailor offers, increasing customer spend per visit by 9%.
- Quantitative Impact: This AI-driven approach has reduced waste by 15% and improved delivery efficiencies by 20%.
- Revenue Impact: In 2023, delivery contributed to 8% of total U.S. sales, up from 3% in 2019, showing the increasing importance of omnichannel strategies.
Future Outlook: Growth, Sustainability, and Digital Transformation
Continued Global Expansion: Starbucks is heavily investing in expanding its presence in China, where coffee consumption is on the rise. In India, where tea dominates, Starbucks has started tailoring its menu to local preferences.
Sustainability Initiatives: Starbucks remains committed to sustainability, with goals to reduce carbon, water use, and waste by 50% by 2030. Their “Greener Stores” initiative will ensure 10,000 stores globally are eco-friendly by 2025.
Digital and AI Innovation: The continued growth of its digital ecosystem, integrating AI and personalized marketing, positions Starbucks to lead in the retail-tech space. The expansion of drive-thru-only stores and mobile-centric models will cater to evolving consumer needs for convenience.
Business Growth Of Starbucks Corporation Over The Years
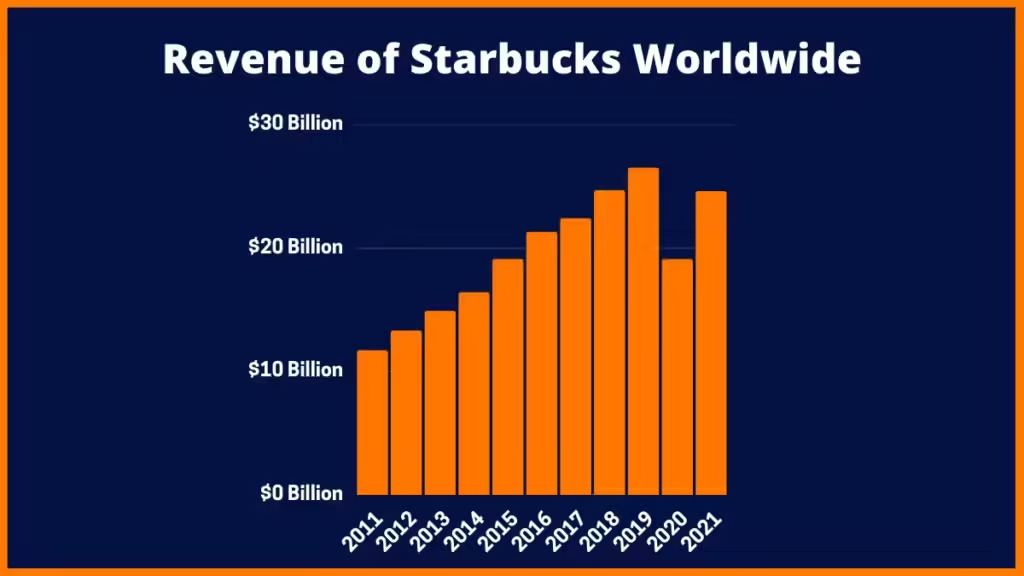
In FY21, despite adding 40 stores, Tata Starbucks saw a 33% year-on-year drop in revenue due to COVID-19. However, the recovery after the second wave was stronger than after the first, with 120% growth in Q2 FY22 compared to the previous year. The company focused on home deliveries, which contributed to 18% of total sales. New offerings include ice cream flavors, a Sanjeev Kapoor menu, and at-home coffee options.






