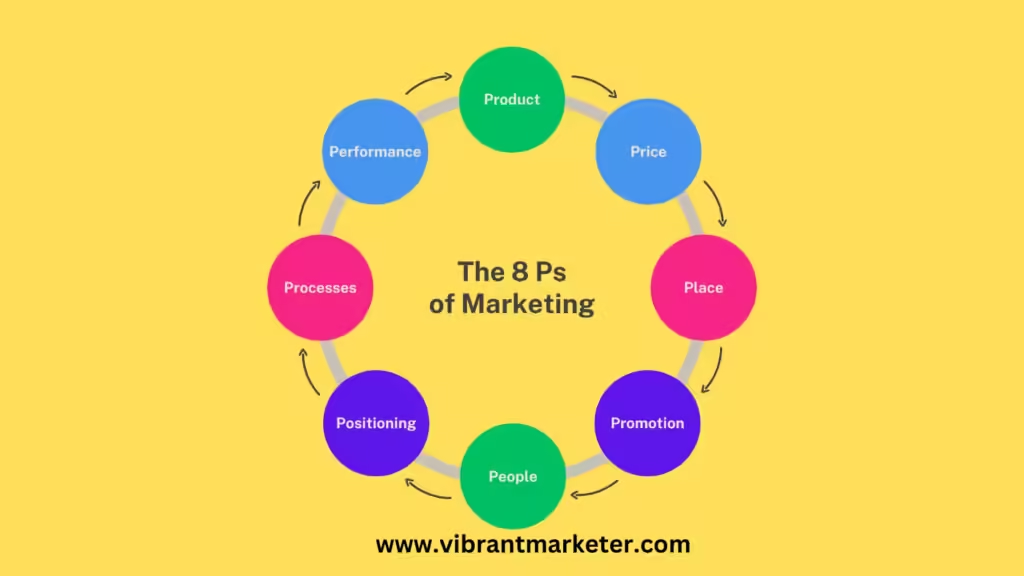
The 8 Ps of Marketing: A Comprehensive Guide to Sales Success
The 8 Ps of marketing with examples are critical tools that businesses use to develop strategies that not only attract customers but also keep them loyal. Let’s dive deeper into each P with real-world Indian case studies, specific sales techniques, and visual ideas that will help you understand these concepts better.
1. Product – What Are You Offering?
A product is the solution to your customer’s problem. It can be a tangible item, a service, or even an experience.
Specific Example: Think about Tata Tea, which did more than just sell tea—it created the “Jaago Re” (Wake Up) campaign. The campaign didn’t just promote a product; it inspired Indians to be more aware of their political rights and social issues. The tea became associated with positive change, making the product more valuable to consumers.
Case Study: Ola Cabs started as a simple taxi service, but it expanded its offerings to include luxury rides, shared services (Ola Share), and even Ola Electric. This product diversification helped Ola serve different types of customers, whether they wanted a budget ride or an eco-friendly one.
Sales Strategy:
- Cross-Selling: Encourage customers to buy additional products. For example, if you run a bookstore, you could recommend journals, pens, or even a reading light as additional items when someone buys a book.
2. Price – How Much Does It Cost?

Your pricing needs to match both the worth of your product and what your customers are comfortable paying.
Specific Example: Reliance Fresh offers competitive prices on groceries, which appeals to price-sensitive customers. They also have premium options for those looking for higher-quality items, giving a wide pricing range to suit different buyers.
Case Study: Swiggy initially attracted users by offering heavy discounts on food delivery. Over time, they introduced Swiggy SUPER, a subscription service that offers free delivery and additional benefits for a monthly fee. This pricing strategy helped Swiggy retain loyal customers and create a steady revenue stream.
Sales Technique:
- Bundling: Offer a package deal for multiple items at a slightly lower price. For example, Pizza Hut offers meal combos (pizza + drink + dessert) that are more affordable together than buying each item individually.
3. Place – Where Is Your Product Sold?
It’s about ensuring your product is accessible to customers at the right time and place when they need it.
Specific Example: D-Mart, an Indian supermarket chain, has become successful by strategically placing its stores in growing residential areas. They focus on high-volume sales and lower profit margins, ensuring products are easily accessible to their target customers.
Case Study: Chumbak, an Indian lifestyle brand, started by selling quirky souvenirs in tourist spots. As their popularity grew, they expanded into online retail and standalone stores in malls, giving them a larger presence.
Sales Strategy:
- Channel Expansion: If you’re a small business, consider partnering with online platforms like Amazon or Flipkart to reach more customers.
4. Promotion - How do you spread the word and let people know about your product?

Promotion is the way you communicate the value of your product to your customers.
Specific Example: Cadbury Dairy Milk has used emotional advertising for years. One of their memorable campaigns, “Kuch Meetha Ho Jaaye,” connected the product with celebrations and happiness, making it a staple during festivals and special occasions.
Case Study: Bajaj Pulsar, a bike brand targeting young Indian men, became popular due to its energetic promotion. The brand used sports sponsorships, thrilling commercials, and stunts to position itself as the bike for adrenaline lovers. it definitely help them to capture the major share in the market .
Sales Technique:
- Influencer Marketing: For smaller brands, partnering with local influencers on Instagram can help you reach a wider audience without spending a lot of money. Many small cafes and boutiques in India use this strategy to build brand awareness.
5. People – Who Makes It Happen?
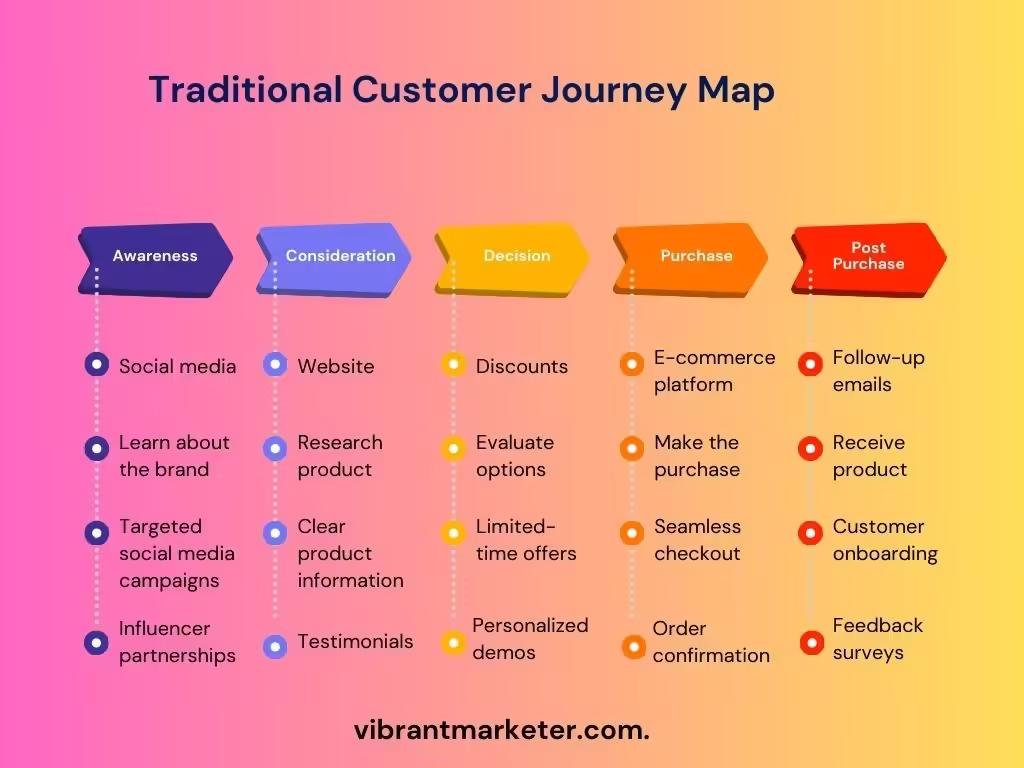
This includes your employees, customers, and anyone involved in the production, sale, or use of your product.
Specific Example: At Infosys, employee engagement is critical. The company invests heavily in training programs, making sure that its people have the skills and tools to succeed. This leads to better client relationships and stronger customer satisfaction.
Case Study: Zappos, an online shoe retailer (though not Indian, the lesson applies), is famous for its focus on employee satisfaction. By keeping its employees happy and motivated most of the times , Zappos delivers exceptional results regarding – customer service. Indian companies like Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) have adopted similar strategies to enhance their workforce performance.
Sales Strategy:
- Referral Programs: You should definitely reward your customer either by cash discounts , coupons if they bring new customer. For example, many Indian e-commerce companies, like Myntra, offer discount coupons to customers who refer their friends.
6. Processes – How Is It Delivered?
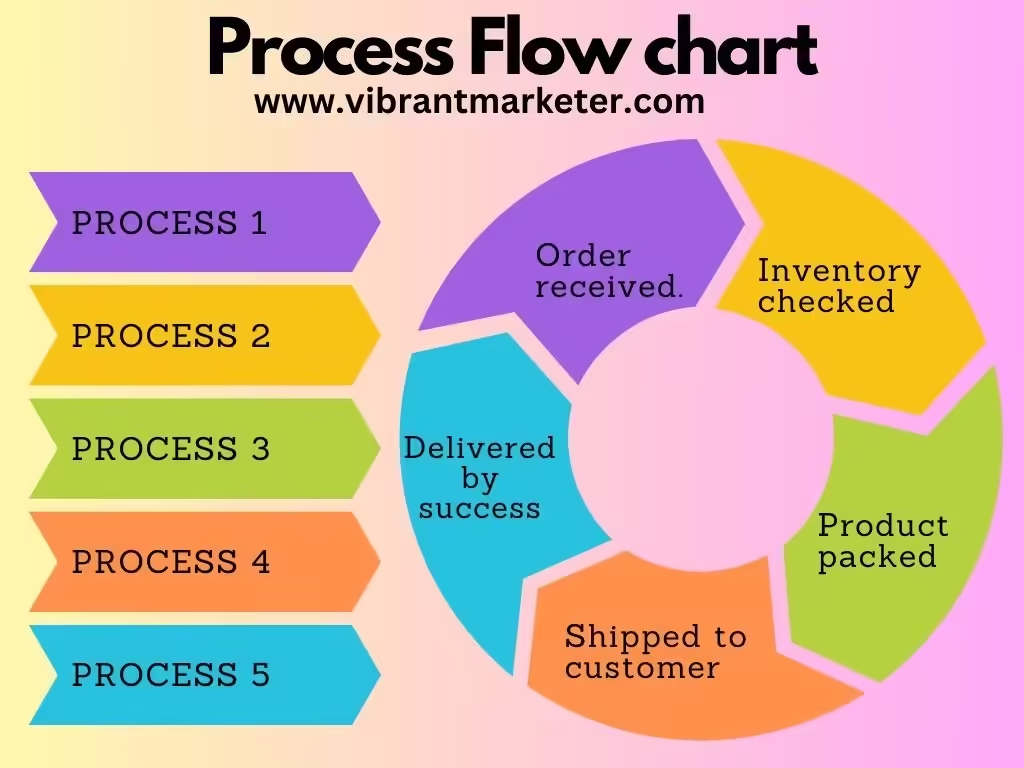
This refers to the operational side of things, ensuring that your product or service is delivered smoothly.
Specific Example: Domino’s Pizza focuses on a streamlined process to ensure that pizzas are delivered within 30 minutes. They use technology to track orders and optimize routes for delivery drivers, ensuring fast service.
Case Study: Flipkart’s success is largely based on its seamless logistics process. From order placement to delivery, Flipkart has created a system that allows it to deliver goods across the country, even to remote areas.
Sales Technique:
- Simplified Checkout: Whether online or in-store, make the payment process quick and easy. For instance, e-commerce platforms like Nykaa offer multiple payment options, including UPI, credit cards, and cash on delivery.
7. Positioning – What’s Unique About Your Brand?

Positioning is how your product is perceived in the market compared to competitors.
Specific Example: Paper Boat, a beverage brand in India, positioned itself uniquely by offering traditional Indian drinks like Aam Panna and Jaljeera in modern, convenient packaging. They played on nostalgia while focusing on health-conscious millennials.
Case Study: Maggi noodles positioned itself as a quick and easy snack for kids and adults alike. Despite facing setbacks during the food safety controversy in 2015, Maggi repositioned itself with stronger quality assurances and reclaimed its market dominance.
Sales Strategy:
- Storytelling: Build a narrative around your brand. For example, Tata Salt positions itself as “Desh Ka Namak” (The Nation’s Salt), highlighting its purity and trustworthiness.
8. Performance – How Well Is It Doing?
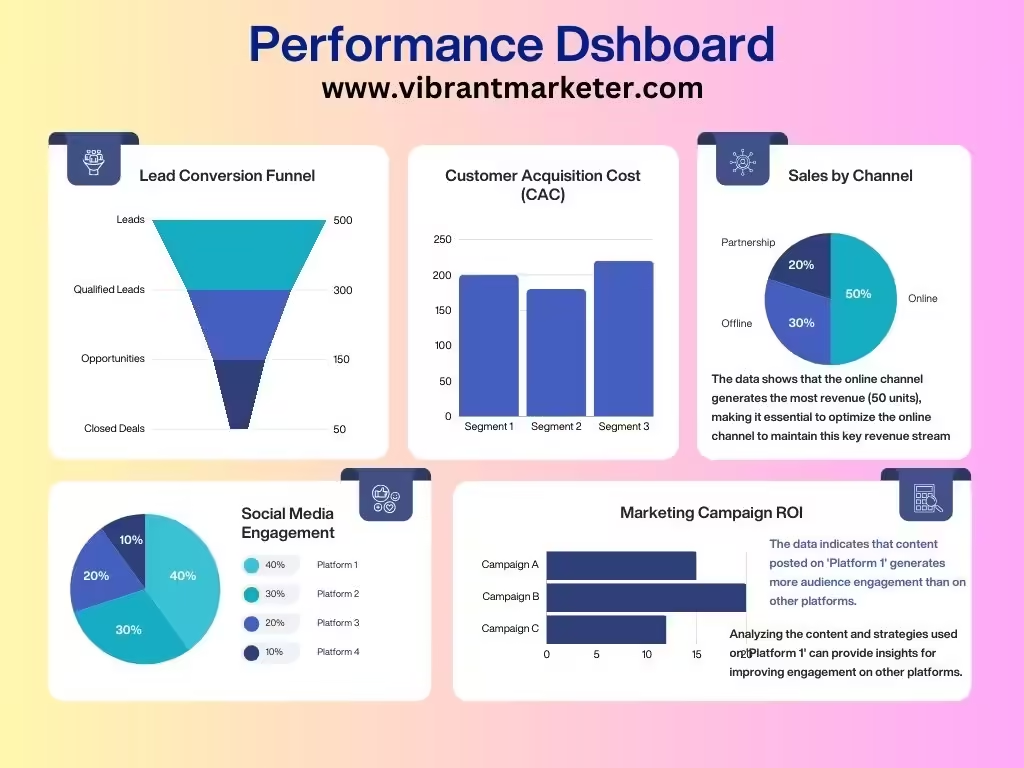
Performance focuses on how your product is performing in the market, in terms of sales, customer feedback, and overall satisfaction.
Specific Example: Paytm has grown from a simple mobile wallet into a full-fledged financial platform, expanding into banking, insurance, and stock trading. They regularly evaluate their performance through customer feedback and financial reports.
Case Study: Asian Paints tracks its market performance through customer insights and data analytics. By doing so, they can offer new products and services, such as waterproofing solutions, to meet changing market demands.
Sales Technique:
- Data-Driven Sales: Use tools like Google Analytics to track customer behavior on your website and adjust your sales strategies accordingly.