What is a Sales Campaign? Detailed Overview with Example
What is a Sales Campaign?

Sales campaigns are often time-limited and focus on achieving specific sales goals, like selling a certain number of products, reaching a certain audience, or introducing a new product. Let’s dive into the details of what makes a sales campaign successful and look at some real-world examples and tips along the way.
- Example: Big Bazaar’s “Wednesday Bazaar” Campaign
Big Bazaar, one of India’s popular retail chains, launched the “Wednesday Bazaar” campaign. The idea was to drive foot traffic to their stores mid-week by offering steep discounts on groceries, household items, and apparel every Wednesday. By giving customers a reason to shop during a less busy time, they increased sales on Wednesdays and improved customer loyalty.
Key Elements of Success:
- Clear Goal: Increase store traffic mid-week.
- Target Audience: Middle-income families looking for budget-friendly shopping.
- Unique Offer: Exclusive discounts only available on Wednesdays.
- Promotion: Ads on TV, radio, and social media announced the discounts.
- Outcome: Customer footfall increased on Wednesdays, and “Wednesday Bazaar” became widely recognized.
- Starbucks Holiday Red Cup Campaign
The Campaign: Every holiday season, Starbucks releases special red cups and seasonal drinks. This limited-time campaign has become a tradition, creating excitement and driving customers to stores.
Objectives:
- Increase Sales Volume: People buy more drinks during the holiday season.
- Build Brand Loyalty: By creating something special for the holidays, Starbucks strengthens its connection with customers.
Results:
- Starbucks sees a major increase in holiday drink sales each year, with long lines in stores and customers sharing photos of their red cups on social media, creating free advertising.
Key Elements of a Sales Campaign
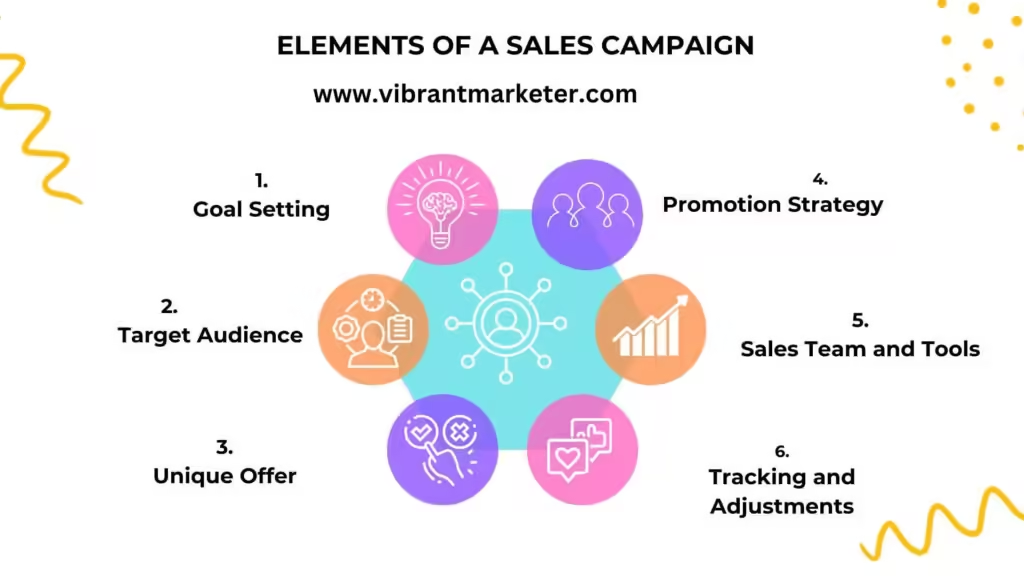
- Goal Setting
- What It Means: The company sets a clear goal for what they want the campaign to achieve. It could be something like “increase sales by 20% this month.”
- Example: Suppose a toy store wants to sell more board games during the holiday season. Their goal might be “sell 500 board games in December.”
- Target Audience
- What It Means: This is all about knowing who the campaign is for. The target audience includes people who would likely be interested in the product.
- Example: If a sports shop runs a campaign for football gear, they would target football fans, young athletes, or parents of kids who play sports.
- Unique Offer
- What It Means: Every campaign has something special, like a discount, a limited-time offer, or a new bundle.
- Example: McDonald’s might offer a special combo at a lower price for a month, making it unique to that campaign.
- Promotion Strategy
- What It Means: This is how the campaign reaches its audience, whether through online ads, social media, email, or in-store displays.
- Example: If the campaign is about a clothing sale, the company might send emails to past customers and post on Instagram to attract young buyers.
- Sales Team and Tools
- What It Means: Companies often rely on their sales team and use tools like customer relationship management (CRM) software to manage and track the campaign’s success.
- Example: Sales teams can use CRM tools like Salesforce to keep track of how many customers responded to the campaign emails.
- Tracking and Adjustments
- What It Means: Throughout the campaign, companies monitor its progress and make changes as needed to improve results.
- Example: A company might notice that their Instagram ads are getting more attention than their Facebook ads, so they could shift more of the budget toward Instagram.
Types of Sales Campaigns
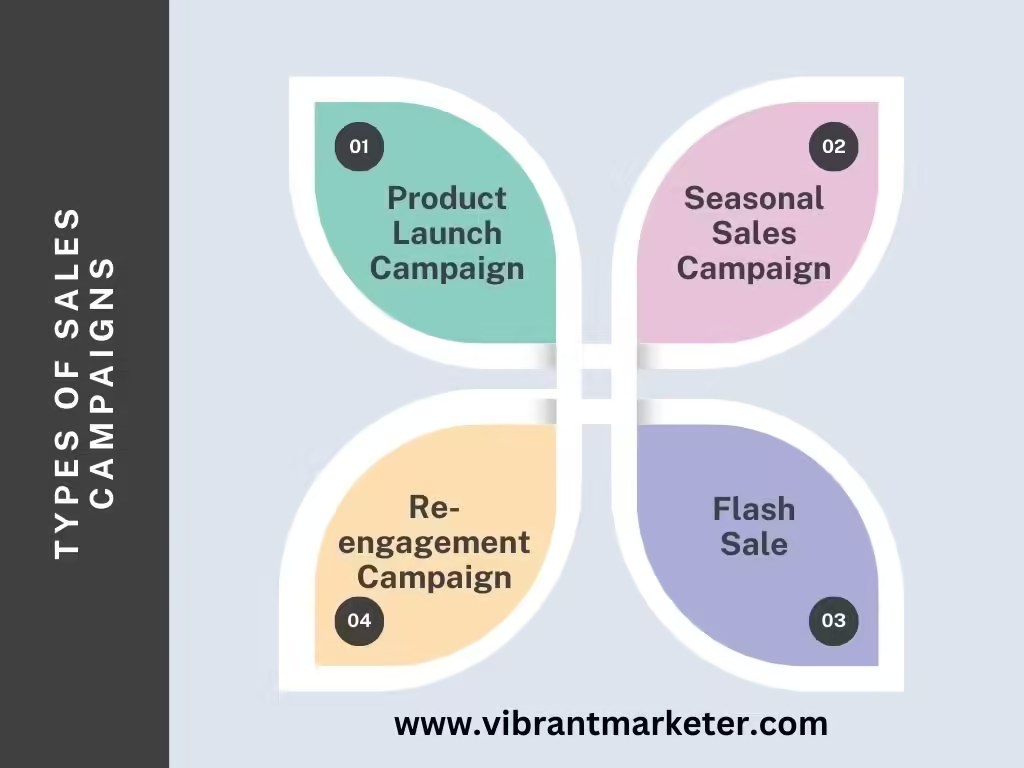
- Product Launch Campaign
- Description: This is used to introduce a new product to the market.
- Example: When Apple launches a new iPhone, they run a campaign with videos, in-store events, and exclusive discounts for early buyers.
- Seasonal Sales Campaign
- Description: These campaigns are common around holidays or special seasons, like Christmas, summer, or back-to-school.
- Example: Amazon’s “Prime Day” is a big seasonal campaign with discounts on thousands of items for Amazon Prime members.
- Flash Sale
- Description: A short, time-limited sale offering big discounts to encourage quick purchases.
- Example: Clothing brands like H&M often have flash sales on weekends, where items are heavily discounted for just a day or two.
- Re-engagement Campaign
- Description: This is aimed at customers who haven’t interacted with the brand in a while.
- Example: A gym might send a re-engagement campaign to past members, offering a special rate to rejoin.
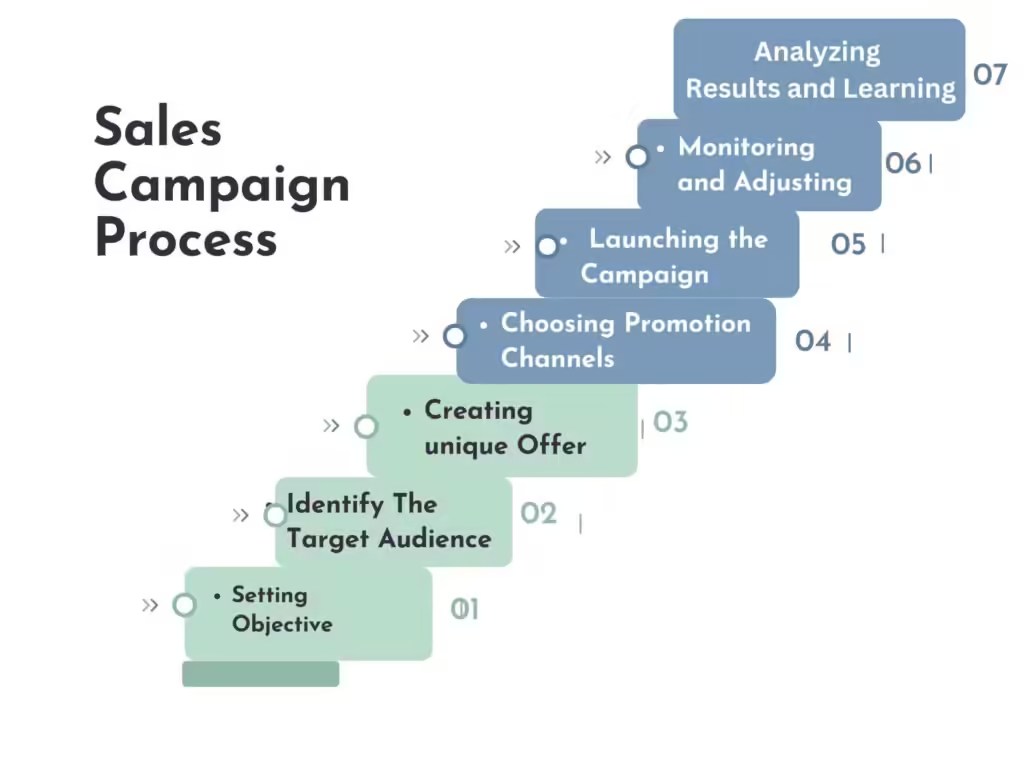
Sales Campaign Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
A sales campaign is like a special event where a company tries to sell a product or service in a fun, targeted way. This involves planning, goal-setting, creating offers, choosing ways to promote, and measuring how well everything worked. Think of it like setting up a lemonade stand – you’d need to make a plan, decide on your price, make signs to attract people, and see how much you sell at the end!
Let’s explore the steps, objectives, and everything else that goes into a successful sales campaign, with real-world examples, data points, and tips to make it easy to understand.
Step 1: Setting Clear Objectives
What It Means: Before launching a campaign, it’s important to know exactly what you want to achieve. Objectives could be to boost sales, attract new customers, increase brand awareness, or promote a new product. Clear objectives help the campaign stay focused and give a way to measure success.
Example: When Nike launches a campaign for a new running shoe, their objective might be to sell 100,000 pairs within a month.
Fun Fact: Studies show that campaigns with specific goals are 42% more likely to succeed.
Step 2: Identifying the Target Audience
What It Means: The target audience is the group of people most likely to buy the product. Identifying the target audience helps the company create a message that speaks directly to the needs and interests of that group.
Example: For a back-to-school campaign, a stationery brand might target students, parents, and teachers.
Data Point: 70% of consumers are more likely to buy if a campaign message feels personalized.
Tip: Use customer surveys or feedback to understand who’s interested in your product and why.
Step 3: Creating a Unique Offer
What It Means: A unique offer gives people a reason to buy now. This could be a discount, a free trial, a buy-one-get-one-free deal, or even a limited-edition product. Offers add excitement and urgency to the campaign.
Example: McDonald’s offers a limited-time “Buy 1 Get 1 Free” deal on burgers. This kind of offer brings in more customers who might buy other items too.
Case Study: Amazon’s Prime Day is a major sales event where only Prime members get access to big discounts. This unique offer not only attracts new customers but also increases membership subscriptions for Amazon Prime.
Step 4: Choosing Promotion Channels
What It Means: Promotion channels are the different places where the campaign is advertised, like social media, email, TV, or in-store posters. The channels should match the audience. For example, younger audiences might see ads on Instagram or YouTube, while older audiences might respond better to emails.
Example: A company promoting a video game might focus on platforms like Twitch and YouTube, where gamers often hang out.
Data Point: Social media ads can increase engagement by 25% for campaigns targeting younger audiences.
Tip: Use different channels to reach different parts of your audience. For example, use social media ads for younger buyers and email newsletters for professionals.
Step 5: Launching the Campaign
What It Means: Once everything is ready – objectives set, target audience defined, offers created, and channels chosen – it’s time to go live! Launching is the kickoff moment when the campaign is officially visible to the public.
Example: When Apple launches a new product, they often create a lot of excitement by showing ads on TV, social media, and their website all at once.
Fact: A well-timed launch can double sales in the first few days of a campaign.
Tip: Launch your campaign at a time when your audience is most active. For example, if targeting office workers, consider launching during the lunch hour or after work hours.
Step 6: Monitoring and Adjusting
What It Means: Throughout the campaign, companies track how things are going. If something isn’t working, they can adjust by changing the offer, shifting the budget, or focusing more on a specific channel.
Example: If a clothing brand sees that their Instagram posts are performing better than Facebook ads, they might focus more on Instagram to maximize sales.
Data Point: 67% of marketers adjust campaigns in real time based on what’s working best.
Tip: Keep an eye on feedback and sales numbers, and make quick adjustments if you see something needs improvement.
Step 7: Analyzing Results and Learning
What It Means: Once the campaign ends, companies review the results to see if they achieved their objectives. They check data like sales numbers, new customers, and ROI (return on investment) to understand what worked well and what didn’t.
Example: If a cosmetics brand ran a campaign to sell 1,000 lipsticks and sold 1,200, they know it was successful and can plan to repeat a similar campaign.
Case Study: Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” campaign replaced the Coke logo with popular names on bottles, leading to a 2% increase in sales. Coca-Cola analyzed the success of this idea, seeing that people loved finding their names, and repeated the campaign in various countries.
Key Objectives of a Sales Campaign
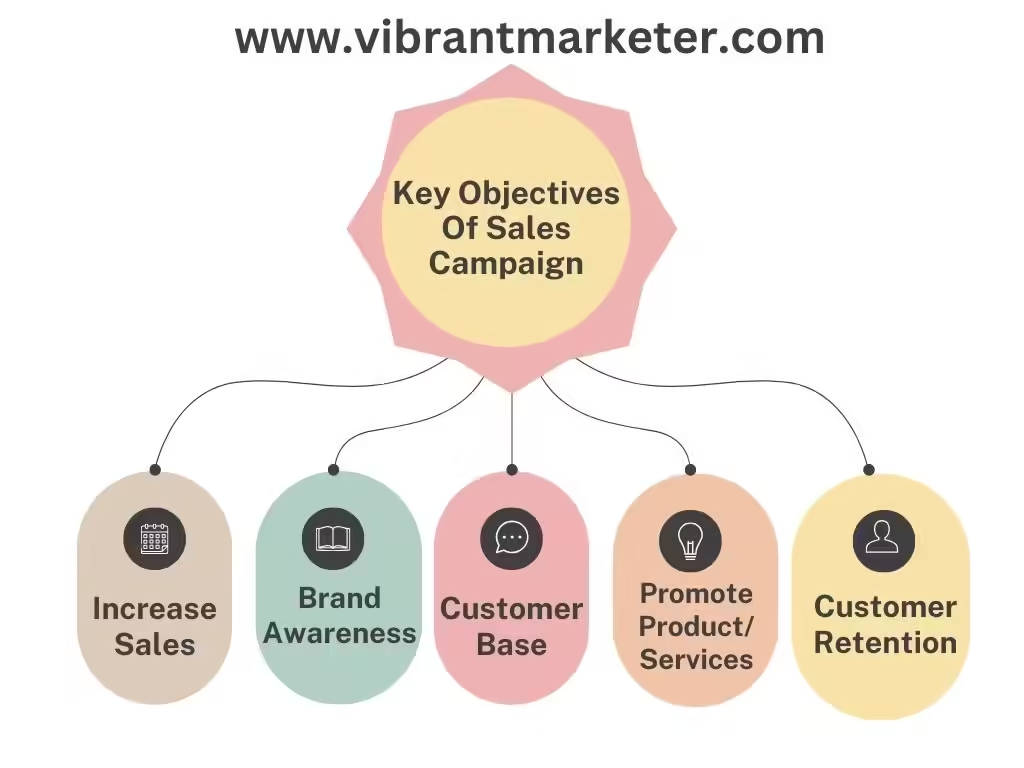
- Increase Sales Volume: The main goal is often to sell more products or services.
- Example: A bookstore runs a holiday campaign with 20% off all children’s books, aiming to sell 5,000 copies by New Year.
- Build Brand Awareness: Campaigns help get the word out about a brand, especially for new products.
- Example: A startup running an ad campaign to introduce a new eco-friendly water bottle might aim to reach 100,000 people through social media.
- Expand Customer Base: Campaigns are a great way to attract new customers.
- Example: A gym offers a 2-week free trial for new members during a New Year campaign to get more people to join.
- Promote a New Product or Service: Some campaigns focus on launching something new.
- Example: A tech company introduces a new smartwatch with a campaign offering free shipping for early buyers.
- Customer Retention: Campaigns can also encourage existing customers to stick around and keep buying.
- Example: Netflix runs a “refer-a-friend” campaign to get current subscribers to bring in new users, offering both a discount.
Key Marketing Strategies in a Sales Campaign

What It Is: Content marketing is the art of creating valuable and relevant content that attracts, engages, and ultimately persuades customers to buy.
- Example: HubSpot, a leading marketing software company, uses its blog, eBooks, and webinars to educate audiences on marketing strategies. By providing valuable insights, HubSpot has attracted millions of followers and built customer trust.
- Data Point: Companies that use content marketing report conversion rates that are six times higher than those who don’t.
- Tip: Create content that answers customer questions or solves their problems. Use various formats like blog posts, videos, infographics, and podcasts to keep the content interesting.
2. Social Media Marketing
What It Is: Social media marketing involves sharing posts, videos, and ads on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and Twitter to reach a broader audience.
- Example: Nike uses social media to showcase its products and connect emotionally with customers through campaigns like “Just Do It.” Nike also uses influencers who resonate with different demographics to reach specific audiences.
- Data Point: Social media users have been shown to spend 27% of their online time scrolling through feeds, making it a powerful platform for brand visibility.
- Tip: Create content that matches each platform’s style. For instance, Instagram is great for visual content, while LinkedIn is better suited for professional, informational posts.
3. Email Marketing
What It Is: Email marketing involves sending emails directly to potential and current customers. These can be product updates, special promotions, or educational newsletters.
- Example: Zara, a fashion retailer, regularly sends emails about their new collections, sales, and fashion tips. This keeps customers informed and excited to shop.
- Data Point: According to studies, every $1 spent on email marketing returns $42 on average, making it one of the most cost-effective channels.
- Tip: Personalize emails with the recipient’s name and send messages based on past purchases or preferences to increase open and click rates.
Sales Campaign Tools and Technologies
The right tools can help you reach customers effectively, measure campaign success, and optimize results.
- HubSpot: This marketing software helps manage content marketing, social media, and email campaigns. HubSpot offers features like customer relationship management (CRM), email templates, and social media monitoring.
- Google Analytics: It provides insights into how users interact with your website, helping identify popular pages and any drop-off points.
- Mailchimp: Mailchimp is an email marketing platform with features like automation, personalization, and audience segmentation. It’s especially useful for small businesses starting email campaigns.
- Hootsuite: This tool manages multiple social media accounts from one place. It allows users to schedule posts and monitor brand mentions.
- Salesforce: Salesforce is a CRM tool that helps track customer interactions across all channels, making it easy to provide personalized service and measure campaign success.
- Data Point: Companies using CRM tools report a 41% higher revenue per salesperson, showing the importance of organized customer information in a successful campaign.
Addressing Challenges and Roadblocks in Sales Campaign Execution
1. Budget Constraints
- Challenge: Allocating the right budget can be challenging, especially for smaller companies.
- Tip: Start with a smaller budget focused on proven strategies. If social media ads perform well, allocate more funds there. Use cost-effective methods like email marketing if the budget is limited.
- Example: Small businesses can focus on social media and email marketing since they are often cheaper and have high engagement rates.
- Challenge: Determining if a campaign was successful can be difficult without tracking.
- Tip: Define key performance indicators (KPIs) from the start. For a social media campaign, KPIs could include likes, shares, and follower growth. For an email campaign, open and click rates are essential metrics.
- Data Point: Only 29% of marketing professionals feel confident in measuring return on investment (ROI) for their campaigns, making this a common struggle.
- Challenge: It’s not easy to grab customers’ attention when they’re constantly bombarded with ads.
- Tip: Use interactive elements like polls, quizzes, and user-generated content to keep your audience engaged.
- Example: Dove’s “Real Beauty” campaign encouraged women to submit photos and share their beauty stories, leading to high engagement and brand loyalty.
- Challenge: Unexpected crises, like product recalls or negative feedback, can damage a campaign.
- Tip: Always have a crisis response plan. Address issues quickly and maintain transparency with customers.
- Example: Southwest Airlines faced a customer backlash due to flight cancellations. Their timely response, transparent communication, and compensation offers helped rebuild trust.
Practical Tips for a Successful Sales Campaign
- Set Clear Goals: Define what success looks like for your campaign. Do you want to increase sales, website traffic, or social media followers? Clear goals will help keep the campaign focused.
- Use A/B Testing: Test different versions of your content, such as two email subject lines or ad visuals, to see which performs best.
- Monitor Results in Real-Time: Use analytics tools like Google Analytics and HubSpot to track the campaign’s performance. Adjust if you notice areas needing improvement.
- Involve the Team: Campaigns require teamwork. Assign roles, from content creation to customer service, so everyone knows their part.
- Optimize for Mobile: With over half of web traffic coming from mobile, ensure your campaign materials (emails, ads, website) look good on small screens.
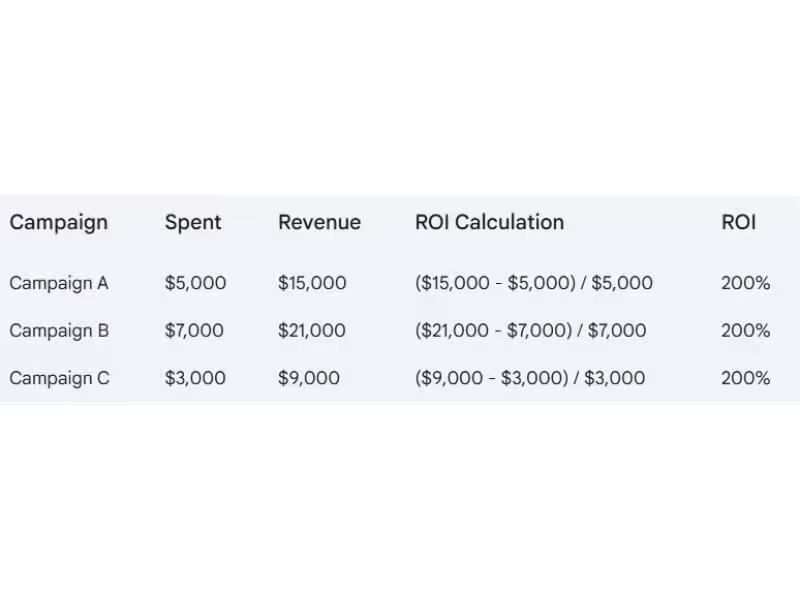
Measuring Sales Campaign Success
Companies measure the success of a sales campaign through metrics like:
- Sales Volume: How many units were sold.
- Revenue Growth: Increase in sales compared to the previous period.
- Customer Acquisition: New customers gained through the campaign.
- Return on Investment (ROI): How much profit was made compared to what was spent on the campaign.
For example, if a campaign spent $5,000 and generated $15,000 in revenue, the ROI would be calculated as: