What is Sales Process Engineering? Brief Overview with Examples
What is Sales Process Engineering?
Example
- Salesforce: Transforming with Data Analytics and AI
Salesforce, a leading company in Customer Relationship Management (CRM), has revolutionized its sales process by using data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI). They analyze large amounts of customer data to spot trends and make more accurate sales predictions. Salesforce also uses AI tools like Einstein AI to identify high-potential leads and recommend the best time to contact them. By doing this, Salesforce shortened its sales cycle, increased conversion rates by around 30%, and improved customer satisfaction.
- HubSpot: Streamlining the Sales Funnel
HubSpot, a company specializing in inbound marketing and sales, transformed its sales process by implementing automation and personalized sales funnels. Using their own software, HubSpot automates repetitive tasks like sending follow-up emails, nurturing leads, and tracking customer interactions. This change reduced HubSpot’s sales cycle by 20%, meaning customers received faster responses, and sales representatives could focus on building relationships instead of administrative tasks.
Specific Strategies Used by Salesforce and HubSpot:
- Data Analytics: Using data to make decisions based on customer behavior.
- AI for Lead Scoring: Prioritizing high-potential customers by predicting who’s most likely to buy.
- Automation: Reducing time on repetitive tasks, allowing sales reps to focus on engaging customers.
Why is Sales Process Engineering Important?
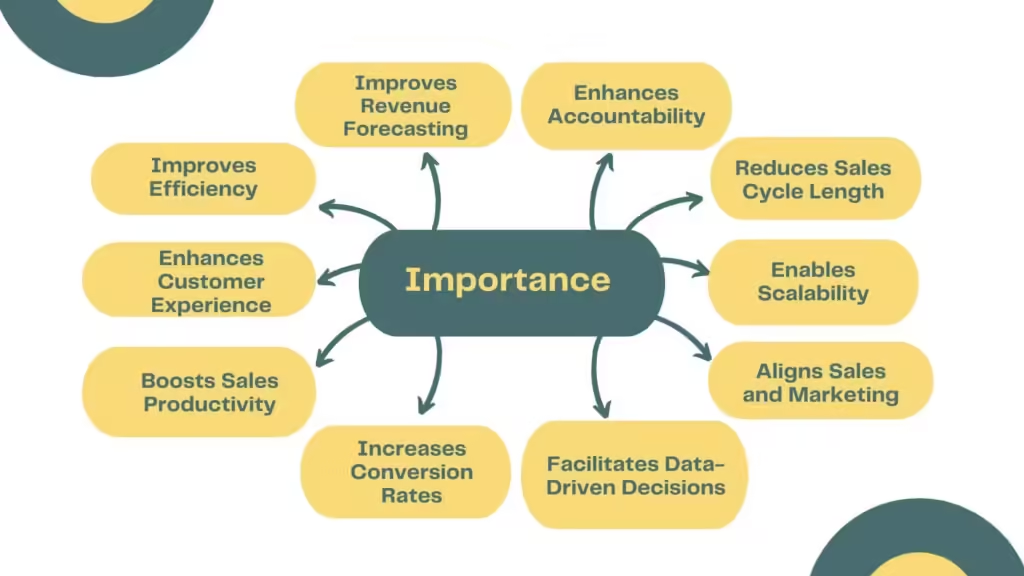
- Improves Efficiency: Streamlines sales tasks, reducing time and resource wastage.
- Enhances Customer Experience: Creates a consistent, positive buying experience.
- Boosts Sales Productivity: Allows sales teams to focus on high-value activities.
- Increases Conversion Rates: Identifies and improves weak spots in the sales process.
- Facilitates Data-Driven Decisions: Uses metrics and data to guide sales strategies.
- Aligns Sales and Marketing: Creates a unified approach, improving lead quality.
- Enables Scalability: Standardized processes make it easier to scale operations.
- Reduces Sales Cycle Length: Speeds up the journey from lead to closing.
- Enhances Accountability: Clearly defined roles and steps ensure team accountability.
- Improves Revenue Forecasting: Standardization helps predict sales outcomes more accurately.
How to Engineer a Sales Process
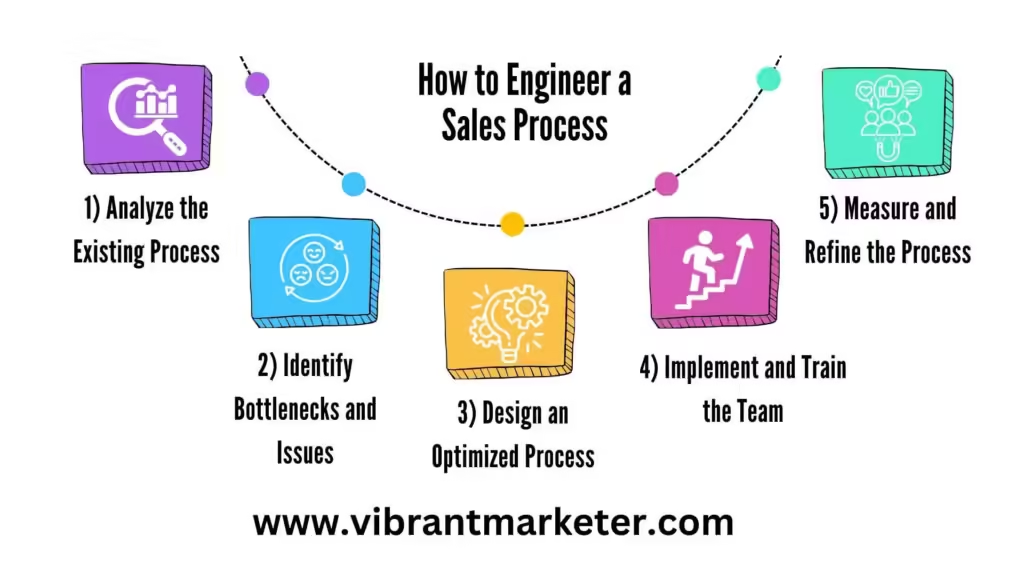
- Analyze the Existing Process
Collect data on how the current sales process performs. For example, let’s say a company, ABC Corp., has a conversion rate of 10% (meaning 1 out of every 10 leads results in a sale). By analyzing each step, they might find that they lose 40% of leads in the qualification stage, signaling a potential area for improvement. - Identify Bottlenecks and Issues
A bottleneck is a point in the process where things slow down. For instance, ABC Corp. finds that their sales team spends too much time on lead qualification, meaning they have less time to close deals. Sales Process Engineering would look for ways to speed up or improve this step, possibly with new tools or additional training. - Design an Optimized Process
After identifying issues, companies can make changes to improve the process. ABC Corp. could introduce a pre-qualification survey for leads, reducing the time salespeople spend on initial calls by filtering out low-potential customers early. - Implement and Train the Team
Even the best-designed process won’t work if the team isn’t trained to use it. ABC Corp. could conduct training sessions to show the sales team how to use the new survey tool and explain the benefits of each process change. - Measure and Refine the Process
To ensure the new process is effective, the company should monitor the results. If ABC Corp. improves its conversion rate to 15%, they know the changes are working. Sales Process Engineering is an ongoing process, meaning that as new data comes in, companies can keep refining their steps.
Advanced Techniques and Tools in Sales Process Engineering
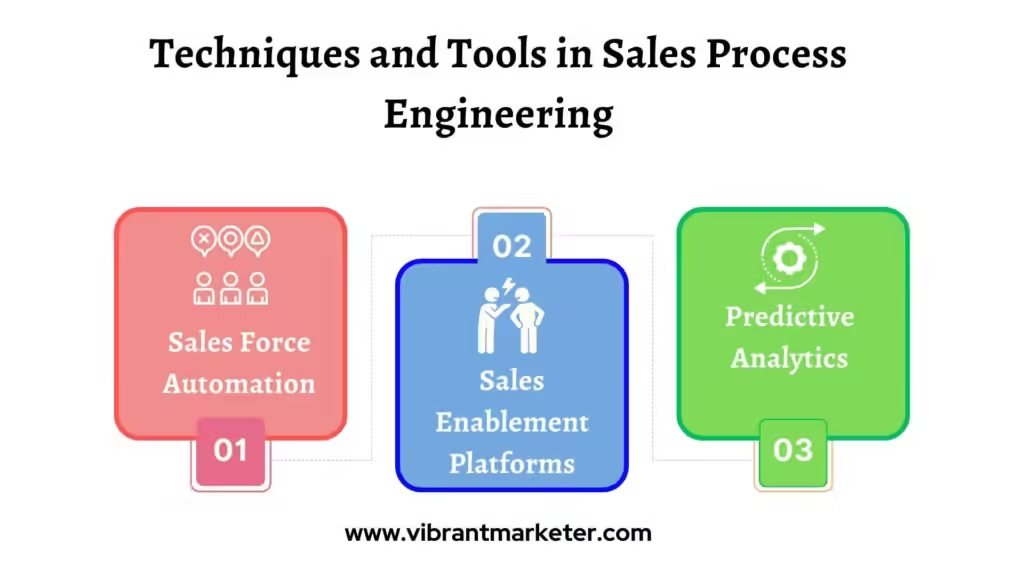
- Sales Force Automation (SFA)
These tools are basically designed to help sales teams automate their repetitive tasks, like data entry, order tracking, and email follow-ups. With SFA, sales reps can save valuable time, which lets them concentrate more on talking to potential customers. For example, an SFA tool might automatically update a lead’s information in the CRM system after each interaction, ensuring the data is always current.
- Sales Enablement Platforms
Sales enablement platforms provide sales teams with the resources they need to be successful, like sales scripts, training materials, and case studies. Think of it like a toolkit filled with all the items a salesperson might need to handle customer questions, create proposals, and close deals. For instance, companies like Seismic offer platforms that store all this information in one place, making it easy for sales reps to access updated content and share it with clients.
- Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses data from past customer interactions to forecast future sales trends. This technique can help identify high-potential leads, showing which customers are more likely to make a purchase. Predictive analytics can boost conversion rates and optimize forecasting. For example, Coca-Cola used predictive analytics to identify which retailers would need specific products, increasing sales and customer satisfaction by ensuring the right products reached the right places at the right time.
The Role of Sales Process Engineering in Digital Transformation
Sales Process Engineering is crucial as businesses adopt digital tools. Digital transformation changes how companies communicate, track, and sell to customers.
- Digital Sales Channels
Using digital channels, like social media, email marketing, and webinars, companies can connect with more customers online. These channels let sales reps reach people who may not visit a physical store but are active online. For example, clothing brand ASOS uses social media to connect with younger shoppers, share product launches, and boost online sales by interacting with customers where they spend time.
- Remote Selling
Remote selling means selling products without meeting customers face-to-face, such as through video calls or online demos. Remote selling became popular during the pandemic, allowing companies to reach customers anywhere in the world. Businesses use tools like Zoom and Microsoft Teams to give product demonstrations, answer questions, and close deals without needing in-person meetings.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRMs, like Salesforce and HubSpot, are used to track customer interactions and store important information about leads. This information helps sales teams remember customer preferences, making it easier to offer personalized recommendations. By organizing customer details, CRMs help salespeople save time and build stronger, long-term relationships with customers.
Measuring and Optimizing Sales Process Performance
To ensure the sales process is working, companies track various performance metrics, also known as Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Conversion Rates: How many leads turn into actual sales.
- Sales Cycle Length: How long it takes to close a deal, from the first customer interaction to the final sale.
- Customer Satisfaction Scores: Ratings from customers about their experience with the company, which can impact repeat business.
Tracking these KPIs helps companies spot which areas of the sales process need improvement. For example, if a company sees that conversion rates are low during the negotiation stage, they can provide additional training to help sales reps handle customer objections better.
- A/B Testing
A/B testing involves trying two different approaches to see which one works best. For instance, a company might try two sales scripts: one that’s more direct and one that’s more conversational. By testing both, they can find out which approach gets better results and make it part of their process.
- Continuous Improvement
Sales Process Engineering is an ongoing process. Companies should review their data regularly and ask for feedback from their sales teams to make sure the process is always improving. Amazon, for example, regularly updates its sales process to align with customer feedback, making its sales process one of the most customer-centric in the industry.
Addressing Common Challenges in Sales Process Engineering
1.Resistance to Change
Sometimes, sales teams resist new changes, especially if they’re used to doing things a certain way. To overcome this, companies can involve sales reps in the decision-making process, showing them how the changes will make their jobs easier or more successful. It’s helpful to provide clear training sessions and explain how new tools or methods will benefit everyone.
2.Data Quality and Accuracy
Data is crucial in Sales Process Engineering, but it’s only useful if it’s accurate. If sales reps enter incorrect information, it can mislead the process and impact results. A simple way to ensure data quality is to train sales teams on how to enter data correctly and conduct regular data audits to catch mistakes early.
3.Integration with Other Business Processes
Sales doesn’t work in isolation; it’s closely connected with marketing, customer service, and finance. If the sales process isn’t aligned with these areas, it can lead to confusion and wasted efforts. For example, if the marketing team promises something that sales can’t deliver, it can create a poor customer experience. Regular cross-department meetings can help ensure everyone is aligned and working toward the same goals.
Data Points and Metrics in Sales Process Engineering
- Conversion Rate: Percentage of leads that turn into customers. A higher rate often means a more efficient process.
- Sales Cycle Length: The time it takes from the first contact with a customer to closing the deal. Shorter cycles mean faster revenue.
- Lead Response Time: How quickly a salesperson reaches out after a lead shows interest. According to InsideSales, leads contacted within 5 minutes are 100 times more likely to convert than those contacted after 30 minutes.
- Customer Satisfaction Scores: Indicates how happy customers are with the process, which can impact referrals and repeat business.
- Revenue Per Sale: Total revenue divided by the number of sales, helping measure the overall value each sale brings.
Tips for Effective Sales Process Engineering
- Gather Feedback Regularly: Ask your sales team what’s working and what’s not. Their insights can reveal valuable process improvements.
- Use Technology: Tools like Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software (e.g., Salesforce) can automate parts of the process, like data entry, so sales reps have more time to focus on selling.
- Set Clear Metrics: Define what success looks like for each step. For example, a “qualified lead” should be clearly defined, so all sales reps evaluate leads consistently.
- Encourage a Customer-Centric Approach: While the process is important, it’s crucial to prioritize the customer’s needs. Train your team to be flexible and responsive rather than overly rigid with the process.
- Refine Continuously: The market changes, and so should the sales process. Regularly analyze data and adjust as necessary.
Benefits of Sales Process Engineering
- Increases Efficiency: Sales Process Engineering cuts down wasted time and effort, helping companies reach their goals faster.
- Improves Customer Experience: Customers feel more valued when sales reps are better organized and prepared.
- Predictable Sales Outcomes: By setting clear steps and measures, companies can better predict their sales performance and make adjustments as needed.
- Better Training for Sales Teams: A structured process provides a clear path for new hires, making training easier and faster.
- Boosts Company Revenue: With a smoother sales process, more leads convert into sales, directly impacting revenue.



